Bull Call Spread

Among the bullish strategies, we find the Bull Call Spread Strategy.
The Bull Call Spread is part of a series of multi-leg strategies that consist of the simultaneous purchase and sale of options with the same expiration but different strike prices.
The Bull Call Spread is a bullish strategy that has a limited maximum profit. The strategy benefits from the rise in the price of the underlying. The trader’s view is bullish.
- It is a strategy that involves buying an In-the-money call and selling an Out-of-the-money call with a strike higher than that of the purchased call. The option’s expiration is the same.
- This strategy is similar to buying a Call Option with the difference that we add a leg that allows us to reduce the cost of the premium paid for the strategy.
- The premium received for the sale of the second call allows us to reduce the cost paid for the purchase of the first.
- The cost of the strategy is represented by the difference between the two premiums.
- A Bull Call Spread is more bullish the more the strike of the sold call is out of the money.
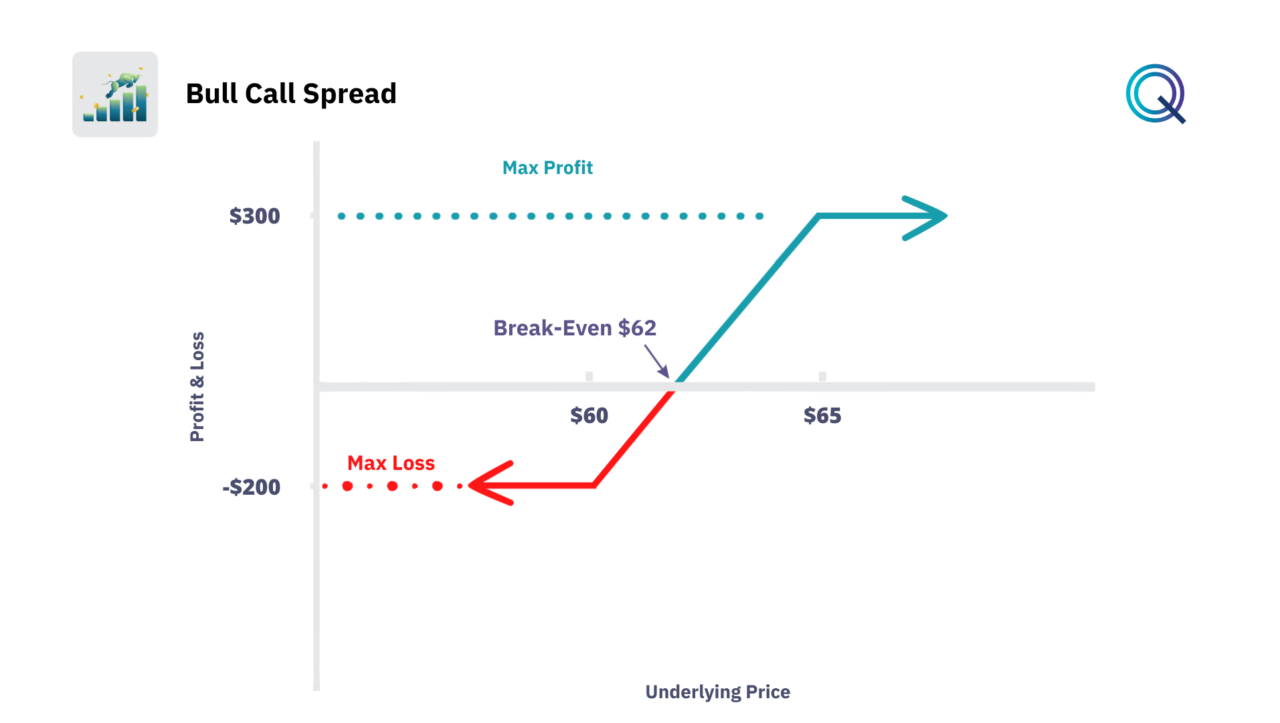
Bull Call Spread Payoff Diagram
Each option strategy has a potential return and a maximum potential loss. These two values can be displayed through the payoff chart. The Bull Call Spread strategy is a debit spread in the sense that this structure has a cost for the trader even though the cost is less than the sole purchase of a call option.
The Bull Call Spread has a payoff diagram with risk and return defined from the time of purchase. Let’s look at this example.
We buy a call option with a strike at $60 and sell a call option with a strike at $65 at a premium of $2.
- Our breakeven price is represented by the strike of the purchased call + the premium paid.
- Our maximum risk is also limited to the premium paid, which is $200 ($2 * 100 shares).
- Unlike the Long Call Strategy, our profit potential has a limit represented by the difference between the two strikes minus the premium paid. In this case, the maximum profit is $300.
The Bull Call Spread is used to take exposure to the underlying through leverage but reducing the risk compared to simply buying a call.
Deep Dive into the Bull Call Spread Strategy
The Bull Call Spread, an alternative approach to bullish options trading, offers investors a way to capitalize on moderate upward moves in the underlying asset with limited risk.
- Cost Management and Profit Potential. The advantage of this strategy is in its cost management. By selling the higher-strike call, the investor offsets the cost of the lower-strike call purchased. The difference in premiums paid and received is the net cost and represents the maximum risk. The Bull Call Spread is particularly attractive when outright calls are prohibitively expensive due to high implied volatility.
- Risk and Reward Trade-off. The trade-off for the reduced initial cost is a capped maximum profit. The best-case scenario is when the underlying asset’s price is at or above the strike price of the sold call at expiration. The profit is the difference between the strike prices minus the net premium paid.
- Market Outlook. The Bull Call Spread is optimal in a market environment where a moderate upswing is anticipated rather than a significant bullish trend. This strategy offers a more conservative profit potential compared to a Long Call due to its defined risk and reward.
- Breakeven and Maximum Loss. The breakeven point is a critical threshold—it’s where the asset price must rise to cover the cost of the spread. Calculated as the lower strike plus the net premium paid, crossing this point means the trade begins to profit. The maximum loss is limited to the net premium paid, making it a risk-defined strategy.
- Volatility and Time Decay. Volatility and time decay are key factors in the pricing of options. A Bull Call Spread benefits from an increase in implied volatility, as it would increase the value of the long call option in the spread. However, because the strategy involves both buying and selling a call, the effects of time decay (Theta) are mitigated. The value of the short call decays at a rate that offsets the decay of the long call.
- Strategic adjustments and exit plans. Traders have the flexibility to adjust the spread in response to market movements. This might involve ‘rolling’ the spread to a further date or adjusting the strike prices. Exiting the position before expiration can capture profits or cut losses, depending on the underlying asset’s price action.
- Incorporating into a Diverse Strategy Portfolio. The Bull Call Spread can be a component of a diversified options strategy portfolio, balancing out more aggressive bullish bets or hedging against other positions. It’s a testament to the adaptability of options for various market conditions.
We talk about this in detail in the Menthor Q Academy.
To recap:
- The Bull Call Spread Strategy is a bullish strategy
- Our position is Long Options
- It is a debit structure
- Our View is bullish on the underlying
- The strategy benefits from an increase in volatility
- Time is a negative factor for this strategy
Other Bullish Strategies
Here are other Bullish strategies with Options:
