The importance of Market Makers

In this article we will describe the importance of Market Makers for the financial markets and why it is key to understand how to read their activity even if we do not trade options. Market Makers move markets.
Market makers engage in delta hedging to manage the risks associated with their trading activities, particularly when they deal with options and derivatives. Delta hedging allows Market Makers to reduce the risks associated with their options trading activities while still earning a profit from the bid-ask spread.
What are Market Makers?
- Market makers are financial companies or individuals who provide liquidity to markets by buying and selling large quantities of securities. They act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers and help facilitate trading by posting bid and ask prices for securities.
- Market makers facilitate trading by providing liquidity to ensure that there is always a counterparty available for traders to execute their orders.
- They profit from the bid-ask spread, which is the difference between the price at which they are willing to buy (bid) and the price at which they are willing to sell (ask) a particular instrument.
- In the stock market, for example, market makers are responsible for providing quotes for stocks they are willing to buy and sell. They are required to maintain a certain level of cash and are often required to have a certain amount of capital to support their trades.
Market makers play a crucial role in the financial markets by providing liquidity and helping ensure that there is always someone willing to buy or sell securities. They help reduce price volatility by providing a source of supply or demand when there are imbalances in the market.
How do Market Makers make money?
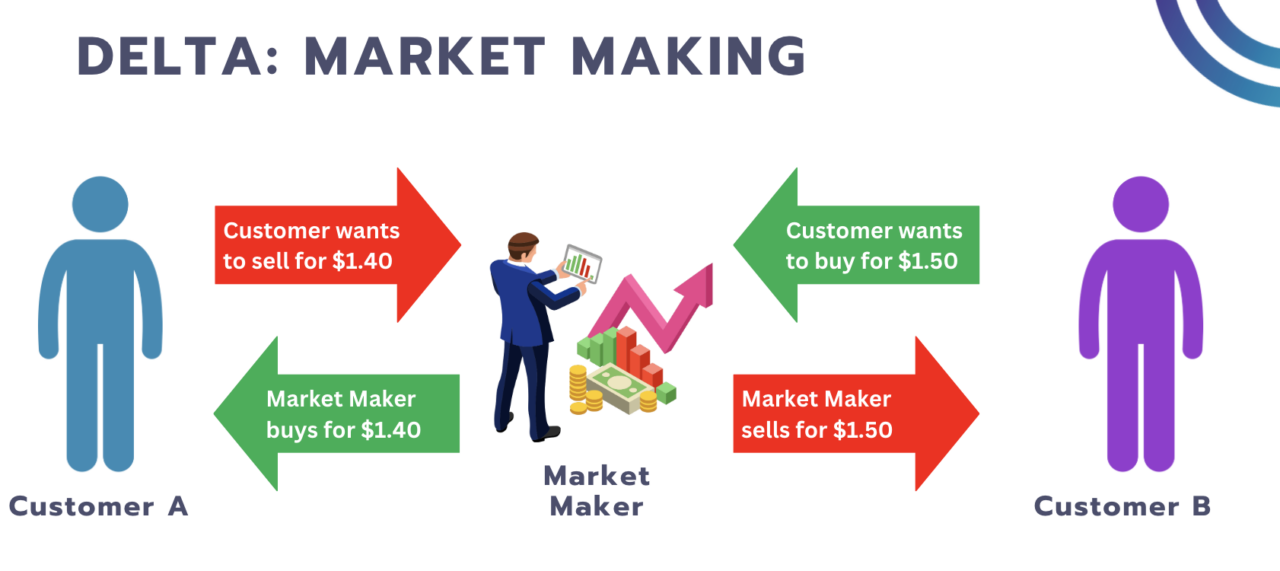
It is important to understand how the market maker makes money. They do not profit from the directionality of an asset’s price. Market makers make money through the spread between the buy (Bid) and sell (Ask) price of a stock. This is called the bid / ask spread.
When they buy a security, they do it at the purchase price and when they sell it, they do it at the sell price. The difference between these two prices is known as the spread and represents the market maker’s profit.
Their risks are associated with price movements and imbalances in their inventory of securities. To manage the risk, they engage in hedging strategies. Market makers may execute offsetting trades in the underlying securities or derivatives to neutralize their exposure to price changes. This activity is what brings more volatility and price movements. By effectively managing their risk, market makers can minimize losses and enhance profitability.
The importance of Market Makers in the Option Market
Market makers are a key element of the financial markets and their importance is higher in the options market, where they play an important role in providing liquidity and helping ensure that there is always a buyer and seller to every option contract.
In the US the majority of Options Trades volumes are executed by Market Makers. Market Makers in the options market are especially important. Here we see a screenshot of the Option Chain of a stock. As an investor, we have thousands of stocks at our disposal. If we think of the US market there are over 12,000 companies listed.
For each stock we have dozens of expirations and hundreds of strike prices. Without a market maker it would be impossible for a buyer or seller to execute their orders.
Delta Hedging and Price impact
Delta hedging by market makers can have an effect on stock pricing, especially in the context of options markets. Here’s how and why it happens:
- Maintaining Delta-Neutral Positions: Market makers engage in delta hedging to keep their options portfolios delta-neutral. This means they balance their long and short options positions by buying or selling the underlying stock. When market makers sell options to customers, they become short (negative delta) those options, which means they are exposed to potential losses if the stock price moves in the opposite direction. To hedge this risk, they buy the underlying stock to offset their short options positions.
- Impact on Supply and Demand: When market makers adjust their positions through delta hedging, it can lead to changes in the supply and demand for the underlying stock. For example, if a market maker has sold a large number of call options (negative delta) and the stock price starts to rise, they will buy the underlying stock to hedge their exposure. This increased buying activity can drive up the stock price. On the other hand, if the stock price falls, they may sell the underlying stock, which can contribute to downward pressure on the stock’s price.
- Feedback Loop: The hedging actions of market makers can create a feedback loop in the stock market. If market makers collectively need to buy the underlying stock to hedge their short positions, this buying pressure can cause the stock’s price to rise. As the stock price rises, more call options may become in-the-money, leading to more delta hedging by market makers, which can further drive up the stock price. This cycle can result in significant price movements.
- Volatility Impact: The delta hedging activities of market makers can also affect stock market volatility. Rapid changes in stock prices driven by delta hedging can contribute to increased intraday volatility, as the market makers adjust their positions to maintain delta neutrality.
It’s important to note that the impact of market maker delta hedging on stock prices is typically more relevant in situations where there is a high concentration of options trading on a particular stock or when there is a significant change in options positions, such as around options expiration dates.
Who are the Largest Market Makers?
In this image you can then see the largest market makers.
- First of all Citadel, founded by Ken Griffin, is certainly one of the most important and profitable funds of recent years. In 2022 they reported 16 billion in earnings. This made them the most profitable Hedge Fund / Market Maker in the world. Citadel became known to the retail world during and after COVID for the Robinhood saga, and for several short squeezes from AMC to GameStop.
- Then there is Two Sigma. It has a portfolio of over $50 Billion. Its market maker does market making for approximately 300M shares per day in the US market.
- Hudson River Trading is a quantitative fund and does market making for approximately 5% of the US market.
All these funds guarantee daily liquidity to the markets. So they are good for the market, but they can also sometimes benefit from them.

